OLED (organic light emitting diode) is a light emitting technology. It is fabricated by a number of thin organic layers between two conductors. When the electricity is provided to them, a bright light appears. These are usually used to make the displays and lighting.

They do not require backlight which is why they are thinner and efficient then LCD displays which need a backlight. Generally, the OLEDs are used in television screens, computer systems and other portable systems. Now research is going on to makewhite OLEDs for solid state lightning applications. The two main families of OLED are those employing polymers and small molecules.
The OLED is the unique light-emitting diode structure with its electroluminescent layer. It is made of carbon-based compounds that emit its own light when electric current flows through it. On the top and bottom there are layers of protective glass or plastic. In between these layers is a negative and positive terminal. There are two layers in them, which are made up of organic molecules called the emissive layer (where light is produced) and the conductive layer. It is said that the OLEDs can achieve higher contrast ratio than LCDs in low ambient conditions.
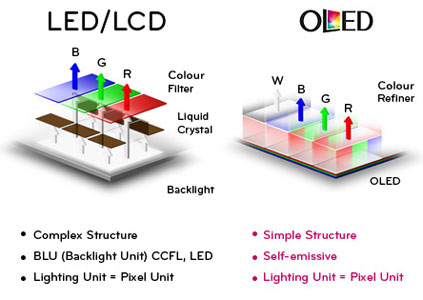
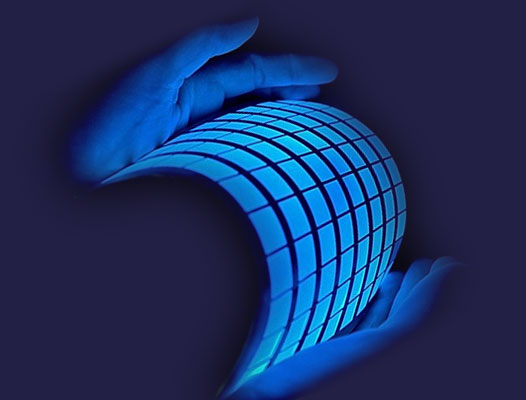
LED is the light emitting diode which produces light because of the movement of electrons through a semi-conductor. LEDS are small but not small enough to be used as pixels on the television. This is why they are just used for backlight. OLED takes less power consumption than LED/LCD. It has a faster refresh rate and has better contrast. The screen or displays have greater brightness with OLED and have a more clear viewing angle. OLED can have different kind of displays which were not available before just like transparent and flexible displays. OLED is longer lasting and durable than LEDs. They can operate in a broader temperature range. Its weight is lighter than LED and the screen from OLED can be made very thin. They can even be printed on flexible surfaces.
Organic Light Emitting Diode is used in many devices these days, which includes mobile phones, computer monitors and large number of TV screens etc. Samsung, Motorola, Nokia, LG are among the largest users of this OLED technology. This is mainly used

by them to produce brighter and more interesting and appealing images. The use of Organic Light Emitting Diode is through solid thin layers which use electricity to create light. It is a very cost effective way of putting in high voltage to the devices. Companies using this technology make the electricity costs low, which makes them more preferred technology than others in today’s world. There are different providers of this technology. Sony Corporation announced that it was beginning OLED screens for its CLIE PEG-VZ90 model of personal-entertainment handhelds. Also, Kodak was the first to release a digital camera with an OLED display. Several companies have are now building computer monitors and large-screen TVs that use the Organic Light Emitting Diode technology.
OLED has many advantages. Some of them are as follows:
There are some limitations of using OLEDs. Some of them are as follows:
Although the life time span of OLEDs are long but this the case with only red and green OLEDs films. But blue organics currently have much shorter life. The manufacturing of OLEDs is expensive.
OLED is subject to burn-in. Like plasma and CRT before it, OLED can retain images on the screen temporarily, and perhaps even permanently, if it's left immobile for too long. The development of the technology is restrained by patents held by Kodak and other companies. For commercial development of OLED technology, it is often necessary to acquire a license.
OLEDs are thin and simple which is why they can be used to create flexible and even transparent displays. It is a really interesting technology and open up to a wide range of possibilities. There are curved OLEDs displays which can be placed on non-flat surfaces. There will be wearable OLEDs available. Transparent OLEDs are expected to be embedded in windows. They can be used in car windshields. New design for lamps will be available in future. There are many more aspects which cannot be imagined yet, but this technology is expected to be produced in a more efficient and effective way in future. There are bright chances of this technology to flourish and make useful changes in the world of innovation.
Sections