B.tech ,ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Sections
Virtual reality industry made great progress in the recent years. Virtual reality uses the combination of optics and computing power to simulate our senses of hearing and sight and gimmicks the brain into believing that we are in a different place. In order to display the virtual reality, Virtual Reality Headsets (it is also called head -mounted display (HMD)) are used.
Virtual reality headset consists of a head motion tracking sensors, stereoscopic head mounted display and stereo sound. Eye tracking sensors and gaming controllers are also associated with some virtual reality headsets. Virtual reality headset replaces the input to our sensors by computer generated information.
ROTATIONAL TRACKING
Rotational Tracking is the capability of a VR headset to trace the movement of your head or your direction of looking. It is done using a motion sensors, accelerometers or gyroscope placed within the headset. Rotational Tracking traces the rotation of head in all the three axes. i.e, Head’s Pitch, Roll and Yaw.

POSITIONAL TRACKING
Positional tracking enables VR headset to trace the orientation of head in a 3D space. The rotational tracking traces only the direction in which you are looking. But, positional tracking makes the VR headset to sense your actions like leaning forward, kneeling down, moving up, jumping etc.
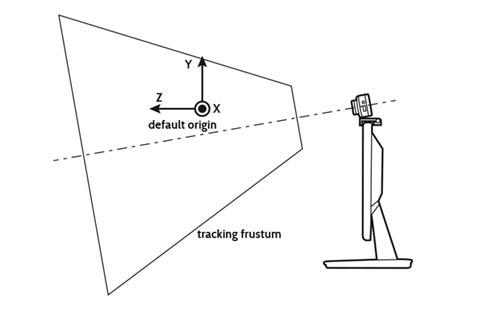
ROOM-SCALE TRACKING
Room-Scale Tracking allows the VR headset to trace every movement of a user in a fixed region. So, you can perform the activities you would like to do in real world such as jump, kneel, crawl etc. without breaking your involvement.

FRAMES PER SECOND (FPS)
FPS is defined as the number of times at which the screen of a VR headset refreshes. For example, 60 FPS means that the screen of the headset refreshes 60 times in a second. In order to experiencing the virtual reality, it is needed to maintain a steady FPS. At low FPS, the user feels a noticeable lag. Then the difference in the movement received by the vestibular system and that received by the eye can makes nausea. In order to avoid this situation and for an immersive VR, 60 FPS is considered as a minimum rate. Then 90 FPS will treat as good and the target set by the VR industries is 120 FPS.
FIELD OF VIEW (FOV)
Field of view is regarded as the actual viewable area. On average, humans are able to see about 170 degrees of field of view. It means that at any instant, we are able to view the world spanning170 degrees around us. But, the FOV drops considerably when we use a VR headset. Therefore, the FOV of a VR headset should be close to 170 degrees as possible to increase the feeling of immersion.
LATENCY
Latency is regarded as delay between the movement of your head and when you see the physical information on the screen. VR headsets have greater dependence on latency. Then the person experiences virtual reality sickness, if the system is slow to respond to the head movement. Latency of 11 milliseconds or less is required for interactive games and 20ms acceptable for VR movie moving around in 360 degree.
RESOLUTION
In virtual reality headsets, a single display is stretched over the large field of view. So, the magnification factor performs significant role. One issue associated with it is screen-door effect. Screen-door effect is described as the visibility of gaps between the individual pixels . This was observable in earlier development kits with lower resolutions.
LENSES
Lenses in the headset have the responsibility for converting the display to an expanded field of view by maintaining the consistency of focus. The problem in consistency causes the drop-off in visual quality from center towards the edges of the display. Since eyes are free to move across visual field, it is needed to avoid refocus and re-accommodate to prevent eye-strain. It provides visual clarity and comfort for the eyes.
ASYNCHRONOUS TIME WARP
Asynchronous Time Warp is a technique used to compensate for the reduction in the frame rate by generating intermediate frames, when the frame rate of the game can't be sustained. Since the visuals with higher frame rate and a necessary low latency causes less nausea than a lower frame rate. Asynchronous Time warp is an adjustment done by morphing the rendered frame with the recent head tracking information before displaying the visuals on the screen. Then the asynchronous time warp helps to reduce the fluctuations.
The limitation of time warp is its dependency on consistency frames. If the system is distracted by another task then the information shown on the headset is far outdated and makes discomfort to the user.
VR HMDs are mainly classified into three categories:
1. MOBILE VR HMDS
Mobile VR HMDs offers rotational tracking. It has a variable FOV of approximately 90 degrees and a variable FPS with maximum of 60 FPS. The popular HMD in this category is the Google Cardboard. It needs a pair of lenses, a magnet, an android phone with a gyroscope and a sheet of cardboard. It provides a better introduction to virtual reality. It is good for viewing 360 degree videos and photos, without moving the head around too rapidly. The input can be provided only by swiping the magnet placed on the side of VR headset. So, this type of headset is better to a user to get a first-time experience in virtual reality. But it is ineffective for providing consistent high quality VR.

2. PREMIUM MOBILE VR HMDS:
It offers positional tracking. It has an FOV of 96 degrees and a consistent 60 FPS. ‘Oculus powered Samsung Gear VR’ headset is an example for this type of VR headsets. Gear VR headset have motion sensors loaded into the headset whereas Google Cardboard uses the sensors present on the phone. Hence, Gear VR headset is able to trace the orientation of head with low latency which provides a consistent FPS. Input is provided through a D-Pad provided on the side of the headset. Since it has an option to attach the controller, these types of HMDs support apps and perform more functionality.

3. TETHERED HMDS:
It offers rotational tracking as well as positional tracking. It has a frame rate of 90 FPS and a FOV of 110 degree. The Oculus Rift, HTC Vive and Playstation VR come under this category. The HTC Vive can also provide room scale tracking within an enclosed 4m x 4m region. It can support complex interactions with the powerful GPU and offer vivid imagery.

APPLICATIONS
MEDICAL TRAINING
VR headsets are used to train surgery procedures for the medical students. Students get chance to perform important procedures of surgeries on the virtual patients and it allows them to get the skills that are needed to perform surgeries on actual patients. It also gives chances to the students to watch the surgery performed by the main surgeon using the virtual reality headset without missing the important procedures.
MILITARY AND LAW ENFORCEMENT
Virtual reality headsets are used to train soldiers by drop them into live exercises with an army having virtual members. It helps them to step into the real world scenarios. It gives a better understanding about how to perform in a battlefield.
Sections